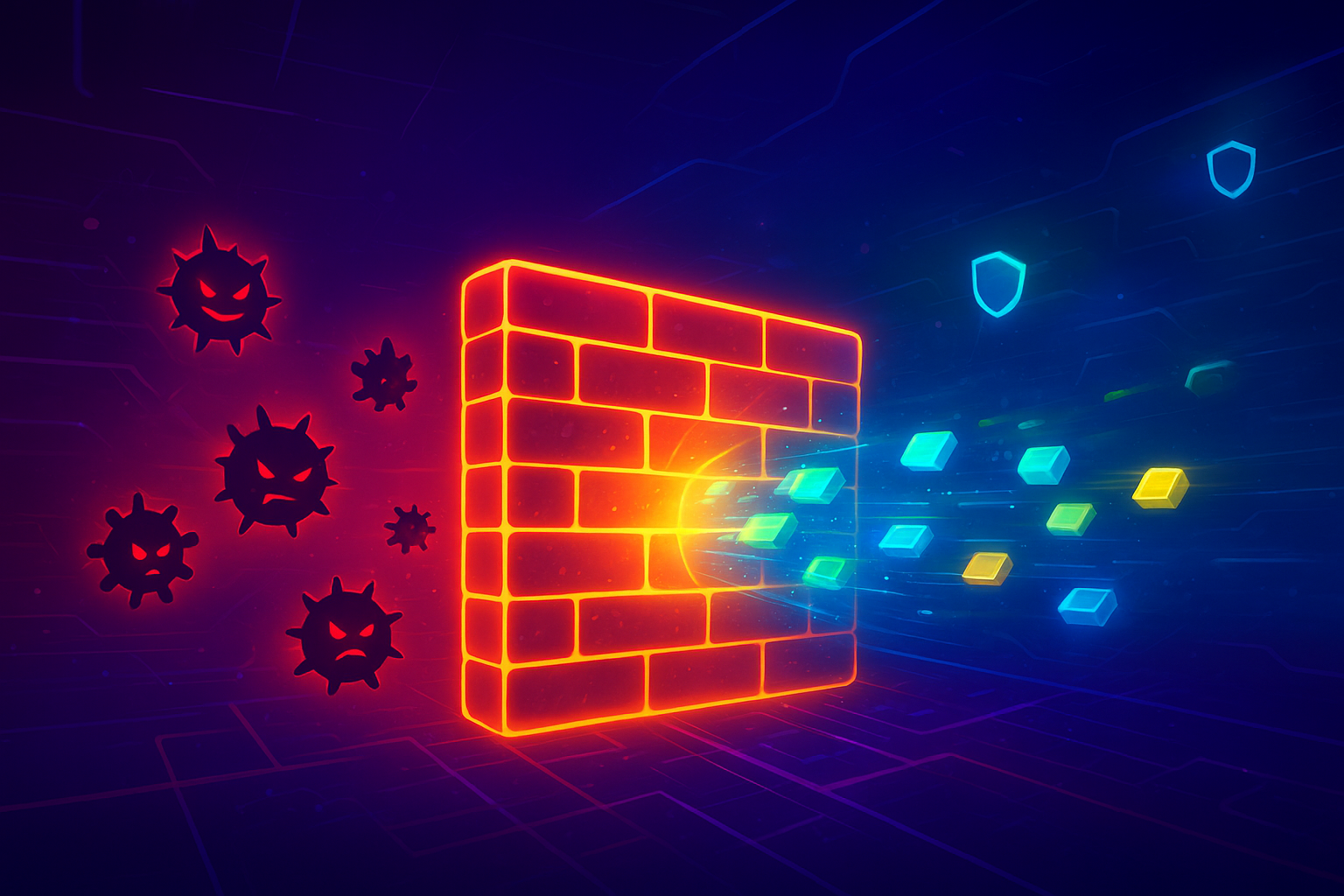
Every click you make online — whether you’re shopping, chatting, or checking emails — sends your data across the internet, where threats like hackers, viruses, and malicious bots are waiting. So how does your device or website stay safe? 👉 The answer is Firewalls — your first and most important line of defense.
🧱 What Is a Firewall?
A firewall is like a digital security guard. It monitors all traffic (data) going in and out of a device or network and decides whether to allow it or block it.
Imagine a security guard standing at the gate:
- ✅ If the visitor is trusted, they are allowed in.
- ❌ If they are suspicious, they are denied entry.
That’s exactly what a firewall does for your device, website, or cloud server.
🔥 Types of Firewalls
1. Software Firewall
- Installed on your personal device (like a laptop).
- Protects only that device.
- Example: Windows Defender Firewall blocks unsafe apps or downloads.
2. Hardware Firewall
- A physical device used mostly in offices or organizations.
- Protects the entire network — all computers connected to it.
- Example: A company installs a firewall near the router to secure all employee computers.
3. Cloud Firewall
- Provided by cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure to protect websites and applications online.
- Example: AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) protects apps hosted on Amazon Web Services.
⚙️ How Does a Firewall Work?
When you access the internet, your data travels in small pieces called packets. A firewall inspects each packet and decides:
- Should it be allowed?
- Is it safe?
- Or is it dangerous and should be blocked?
Firewalls Make Decisions Using Four Key Checks:
🔹 1. IP Address – Who Is Sending the Data?
Every device on the internet has an IP address (like a home address). Firewalls check if the data is coming from a safe or dangerous source. If an IP has a bad reputation or has been used in attacks before, it’s instantly blocked.
🔹 2. Ports and Protocols – Which Door Is Being Used?
Internet services use different ports (channels). For example:
- Web browsing uses port 80 or 443
- Emails use port 25 or 587
Firewalls allow only safe ports and block the rest.
🔹 3. Packet Content – What’s Inside the Data?
Modern firewalls don’t just check who’s sending data — they also inspect what’s inside it.
This is called Deep Packet Inspection:
- The firewall looks inside the packet to detect malware or malicious code.
- If anything harmful is found, it is blocked instantly.
🔹 4. Application Insights – Which App Is Sending This Data?
Next-generation firewalls are smart enough to detect which application is generating the traffic.
They allow trusted apps like Zoom, Gmail, or WhatsApp, and block fake or unknown apps.
💼 How Startups and Small Businesses Use Firewalls
You don’t need big budgets or fancy hardware. Small companies often use:
- Cloud firewalls from AWS, Azure, and Cloudflare
- Software firewalls on their laptops
- Linux firewalls like UFW to protect their servers
🔒 Why Firewalls Still Matter Today
Firewalls protect you from:
- Hackers trying to break in
- Malware and viruses
- Unauthorized access
- Data theft
- Spam traffic and bots
Without firewalls, your system would be wide open to attacks 24/7.
🤖 The Future of Firewalls
Firewalls are getting smarter every day. They now use:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Machine Learning
- Real-time threat detection
- Automatic updates
🎯 Final Thought
Firewalls may not be visible, but they are always working silently in the background, protecting your data and privacy.
They don’t just guard your network — They guard your peace of mind.
Jump into our new LinkedIn thread on Firewalls — The Silent Bodyguards Protecting the Internet and add your experience.
Also, read our last article: Mastering Query Optimization for Faster Databases
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.